Information Management, as per the definition in Bitpipe.com, is “a method to use technology for collecting, processing and condensing information with a goal of efficient management”. Prior to the advent of technology enablers, the information management process involved collecting information through forms made in triplicates or more to ensure that all the functions received the required information to manage their processes. In olden days, information management was as critical as today for running the business, but most of them used paper-based processes. For example, attendance recording with time cards; leave processing was largely managing multiple copies of filled-out leave applications submitted to various departments. In India, even the most technologically advanced organizations were deep into paper-based processes just five years back. Majority of these organizations have recently moved towards automation of the information management processes in Human Resources.
Information management in human resources is the most critical function of an organization and therefore designing any system or process to manage information should adhere to the following guidelines
- Compliance (legal and government) guidelines: For example, if an organization is defined under Factories Act, maintaining the relevant documents (Provident forms; Insurance forms etc.) and publishing periodic reports are mandatory as per the guidelines.
- Organization business process and strategy compliance: Every organization has its own established internal process controls (for example no. of years performance appraisal records required to be maintained etc.) and the information management system should follow these guidelines
- The availability and ease of access to the information management system. Along with meeting the above two criteria, information management system providers of an organization needs to focus intensely in this area, as this feature provides a visible platform to receive and address feedback.
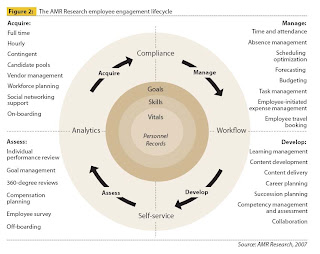
When we look at HR Systems and processes landscape and realize the value it adds to employee experience, the framework for evaluating the relevance of these systems will have to be different. The reason for taking this approach is that it helps us deliver systems and processes employees crave for. Let me explain the difference between the framework presented below with some of the existing frameworks published in recent publications. AMR research, 2007 presents the employee lifecycle and how HR Systems are required to manage various phases of employment such as Acquire-Manage-Develop and Assess. This framework built clearly from the HR Organization perspective and applications required to manage the solutions. Recently Cedar Crestone presented an application blueprint that places applications in the area of Administrative Excellence, Service Delivery Excellence and Performance Excellence. This blueprint looks inwards for the aspects that best suits HR organization and the resulting benefits to the employees.
The model below describes Human Resource Information Management – Layers looks at the HR Systems from employee experience perspective. The model was tested using a sample audience from my friends. The proposed theory is based upon the experiences shared by my colleagues from previous organizations.

Most of the processes in the bottom layer such as Talent Acquisition process; On-boarding process; Leave and Payroll processing and Benefits administration are viewed by the employees as organisation hygiene factors. As a part of my current role, I regularly attend on-boarding HR systems orientation programs for new hires. Majority of the issues faced by new employees relate to on-boarding process. This clearly indicates that an employee expects zero defect rate during on-boarding processes. However, achieving zero defect rate does not give high scoring points towards employee experience. Similarly achieving timely payroll processing and leave management too don’t attract brownie points for employee experience because these processes are necessary basic hygiene factors for any good organization. Talent Acquisition process may not fall into the basic, but one of the concerns faced in Indian organizations is that the organization approached me from multiple locations for multiple positions on regular basis. This definitely can be avoided which in turn will help in avoiding many unpleasant scenarios. Many would agree that this is one of the commonly encountered scenarios. The efficiencies in this process would bring significant improvements in experience for all the parties involved. At the same time it has to be acknowledged that the technology solutions are far from achieving the maturity state in this line.
As we move up the employee experience, we find more around process automation and self service. This empowers the employees distinctly and also helps bring in considerable transparency into the system. To be in control of one’s own develop and administrative tasks contributes to a positive self perception. Some of the most commonly automated processes along with self service feature across industry are the tax declaration; paystub, leave application management, and timesheets. The next level of automation and transparency an employee expects is in the area of performance management. This is an area which when built in a robust and transparent manner immensely helps employee satisfaction. Performance management and its connection to compensation administration are well known. However, very few employees understand the mechanism on how it works. Letting employees see through this process results in better employee experience.
Learning management is another critical area with the potential to improve employee experience and satisfaction. Many a times communication on training plans reaches only the function head level and there onwards it is left to the discretion of whomever the function head nominates to act on the communication. Learning management automation would definitely add to employee experience. It is one of the easiest processes to automate and produces immediate results in employee experience.
The last level in accomplishing employee experience requires focus on employee service center, talent development and career planning, employee surveys and action on the same and efficient off boarding. An interesting reason why off boarding is placed in the last level is because it is at the high end of employee experience and has huge implications on organization branding. Employees are the brand ambassadors of a product wherever they go and a very good off-boarding experience goes a long way in building brand value. I still hold my very first organization in high regard for the way the entire off-boarding process was managed and am very proud to be an alumni of that organization. Successful off-boarding is again a quick win factor like a successful learning management process.
Efficient employee service center is an additional factor towards employee experience. An economics of scale is required to have service center operations and many of the 1000+ employee organizations can afford to build a good service center model to manage employee experience. Many organizations do carry out employee engagement surveys but these surveys stop producing desired results if they are not followed up with well defined action points and follow through. It is much easier to execute a survey than to act on it to bring in employee confidence.
The last topic around with significant amount of research has been done and for which models have been built is talent development and career planning. An effective handling of this area improves employee experience, but very few organizations have meaningful processes for it. This requires culture change from both the employee and the organization.
The item glaring missing in the above model is reporting and analytics. This is because an employee gets minimum benefit from this feature. However, it is one of the most important aspects of any HR Systems model as it enables the organization to measure the success of all the above processes which in turn enables enhanced employee experience. Another important missing item is technology integration. This is a main source for all the troubles plaguing the IT folks as there is no single solution available in the market , which excel in all the blocks and obviously it requires strong technical skills to ensure that we get the best out of these systems.
The above proposed model strongly urges organizations to look at the HR Systems from employee experience index framework rather than from the requirements for HR. Every organization has two halves, one the employee and the other the customer. Organizations are willing to bend backwards to please the customers but the main set of people who are going to look after your customers are employees. If the employees’ needs are taken care, they will bring in the prosperity to the organization.